Originally published in Tufts Now.
BOSTON (Sept. 14. 2020, 9:00 a.m. EDT)—Some but not all U.S. metro areas could grow all the food they need locally, according to a new study estimating the degree to which the American food supply could be localized based on population, geography, and diet.
The modeling study, led by Christian Peters at the Gerald J. and Dorothy R. Friedman School of Nutrition Science and Policy at Tufts University, is published today in Environmental Science & Technology.
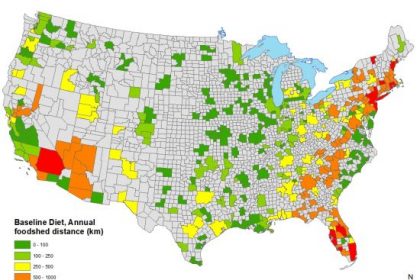
The model estimates whether 378 metropolitan areas could meet their food needs from local agricultural land located within 250 kilometers (155 miles). Local potential was estimated based on seven different diets, including the current typical American diet.
The results suggest:
- Metro centers in the Northwest and interior of the country have the greatest potential for localization.
- Large portions of the population along the Eastern Seaboard and the southwest corner of the U.S. would have the least potential for localization.
- Surplus land existed under all diet scenarios, raising questions about the best use of land for meeting health, environmental, and economic goals.
“Not everyone lives near enough agricultural land to have an entirely local or even regional food supply. Most cities along the Eastern Seaboard and in the southwest corner of the U.S. could not meet their food needs locally, even if every available acre of agricultural land was used for local food production. Yet, many cities in the rest of the country are surrounded by ample land to support local and regional food systems,” said Peters, senior author and associate professor at the Friedman School, whose research focuses on sustainability science.
Peters and his team also modeled seven different diets to estimate whether dietary changes could make a difference in the potential to produce sufficient food for a metro area. The diets ranged from the current typical American diet, which is high in meat, to vegan. Reducing animal products in the diet increased the potential to produce all food locally, up to a point. Diets with less than half the current consumption of meat supported similar levels of localization potential, whether omnivore or vegetarian. Consumption of meat (beef, pork, chicken and turkey) for the baseline typical American diet was estimated at roughly five ounces per day.
“There would be different ways to do it. Imagine, if we cut back to fewer than two and a half ounces per day by serving smaller portions of meat and replacing some meat-centric entrees with plant-based alternatives, like lentils, beans and nuts. More diverse sources of protein could open new possibilities for local food. Nutrition research tells us that there could be some health benefits, too,” said corresponding author Julie Kurtz, who was a master’s degree student at the Friedman School at the time of the study
Under all the diet scenarios, the model projected the United States having a surplus of land for meeting domestic food needs. In the current American agricultural system, some farmland is used for biofuels and export crops. The researchers point out that if metro centers focused on eating locally, many agricultural areas would face new questions about local land use priorities.
“It would be important to make sure policies for supporting local or regional food production benefit conservation and create opportunities for farmers to adopt more sustainable practices. Policies should also recognize the capacity of the natural resources in a given locale or region—and consider the supply chain, including capacity for food processing and storage,” Peters said.
Economic efficiency for food production was beyond the scope of the analysis. Also, the study is based on current conditions and does not consider how future climate change may affect future agricultural potential.
Authors and Funding
Additional authors on the study are Peter B. Woodbury of Cornell University’s College of Agriculture and Life Sciences, Ithaca, NY and Zia U. Ahmed of University at Buffalo, Buffalo, NY.
This work was supported by funding from the W.K. Kellogg Foundation for the project, “Foodprints and Foodsheds: Tools for Evaluating the Sustainability of Dietary Patterns and the Geography of the Food System.” The authors disclosed no conflicts of interest.
Citation:
Kurtz, J.E., Woodbury, P.B., Ahmed, Z.U., & Peters, C. J. (2020). Mapping U.S. food system localization potential: The impact of diet on foodsheds. Environmental Science & Technology. https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acs.est.9b07582
###
About the Friedman School of Nutrition Science and Policy at Tufts University
The Gerald J. and Dorothy R. Friedman School of Nutrition Science and Policy at Tufts University is the only independent school of nutrition in the United States. The school’s five divisions – which focus on questions relating to nutrition and chronic diseases, molecular nutrition, agriculture and sustainability, food security, humanitarian assistance, public health nutrition, and food policy and economics – are renowned for the application of scientific research to national and international policy.




